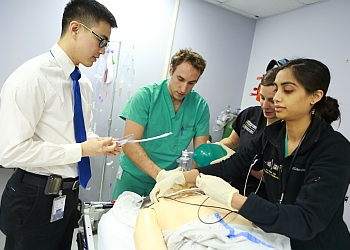
Medical and healthcare simulation is the imitation or practice of clinical situations in an artificially created environment. Students who enroll in the unique, two-year, part-time Master of Science in Medical and Healthcare Simulation (MSMS) program can expect to learn effective simulation and evaluation techniques, curriculum design and how the use of technology can enhance the clinical learning experience. There is much that goes into developing clinical scenarios that will have the most impact on the learner.
How Is a Simulation Scenario Developed?
Healthcare simulation scenarios can be developed to teach learners clinical, teamwork and communication skills. Scenarios may be developed in response to an identified problem or learning gap in an academic or clinical setting. Scenarios should always be developed with the goal of an educational session in mind. Once a problem is identified, goals and objectives for the learning outcomes can be created and a role-playing exercise developed to practice in a safe environment without risk to patients.
Transporting the Learner
The simulation scenario transports the learner into a clinical situation complete with a simulation mannequin that has heart and lung sounds, the ability to sweat and shed tears, and pupils that dilate. Mannequins are designed to allow for practice and mastery of a physical examination as well as other clinical skills, such as placement of an intravenous line and chest tube, delivery of an electrical shock that occurs during cardiac arrest and even childbirth. The simulation room generally has monitors and other equipment similar to an actual hospital emergency or operating room. During the scenario, simulation educators, acting as nurses, doctors or other healthcare workers, are placed within the scenarios to help facilitate a realistic clinical experience.
Learning Without Risks to Patients
The practice of clinical, technical or procedural skills typically involves the use of a mannequin, task trainer or standardized patient to allow learners to practice skills as though they were interacting with a real patient. They learn to better communicate and manage the consequences of their decisions in a safe learning environment without risk to patients. After a patient scenario, the learners are debriefed by a simulation educator who works to help them understand methods for improvement of managing the communication, teamwork and patient care aspects of the case.
What Courses Can I Expect to Take?
The MSMS degree program, through Drexel University College of Medicine’s Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences and Professional Studies, provides students with a core, detailed focus on the many facets of simulation-based medical education. Classes are centered on topics like: methods and practical implementation of medical simulation, instruction in the operation and use of a variety of medical simulation and educational research design. Other courses include:
- Review of the history and theoretical basis of simulation in medical education
- Assessment theory and application
- Simulation curriculum design
- Debriefing
- Teamwork training
- Interprofessional education
There is also instruction on the many different technologies used in medical and healthcare simulation training including, but not limited to, high-fidelity human patient simulators, task trainer simulators, simulation multimedia tools and virtual reality.
Interested? Contact Us
If the MSMS program interests you, please contact us through our program website. You can also email us at MSsim@drexelmed.edu and follow us on Twitter @mssimdrexel.